Risk Management Disclose how the organization identifies, assesses, and manages climate-related risks.
a.Describe the organization's processes for identifying and assessing climate-related risks. b.Describe the organization's processes for managing climate-related risks. c.Describe how processes for identifying, assessing, and managing climate-related risks are integrated into the organization's overall risk management. |
|---|
Climate Change Risk Management
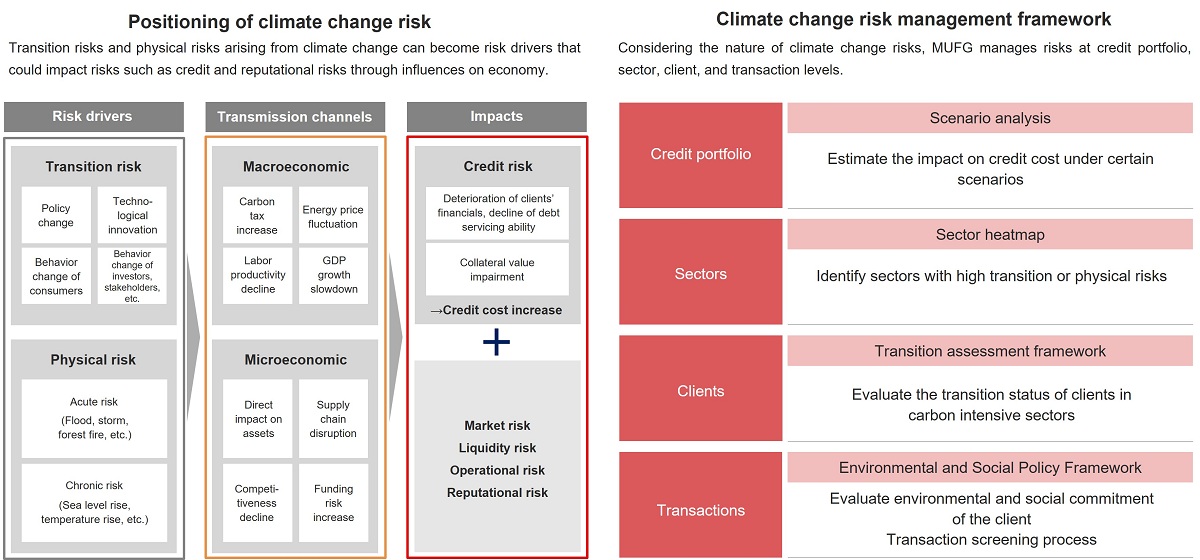
Environmental and Social Risk Management in Finance
- Credit, bond and equity underwriting for corporate clients of MUFG's main subsidiaries, the Bank, the Trust Bank and the Securities HD.
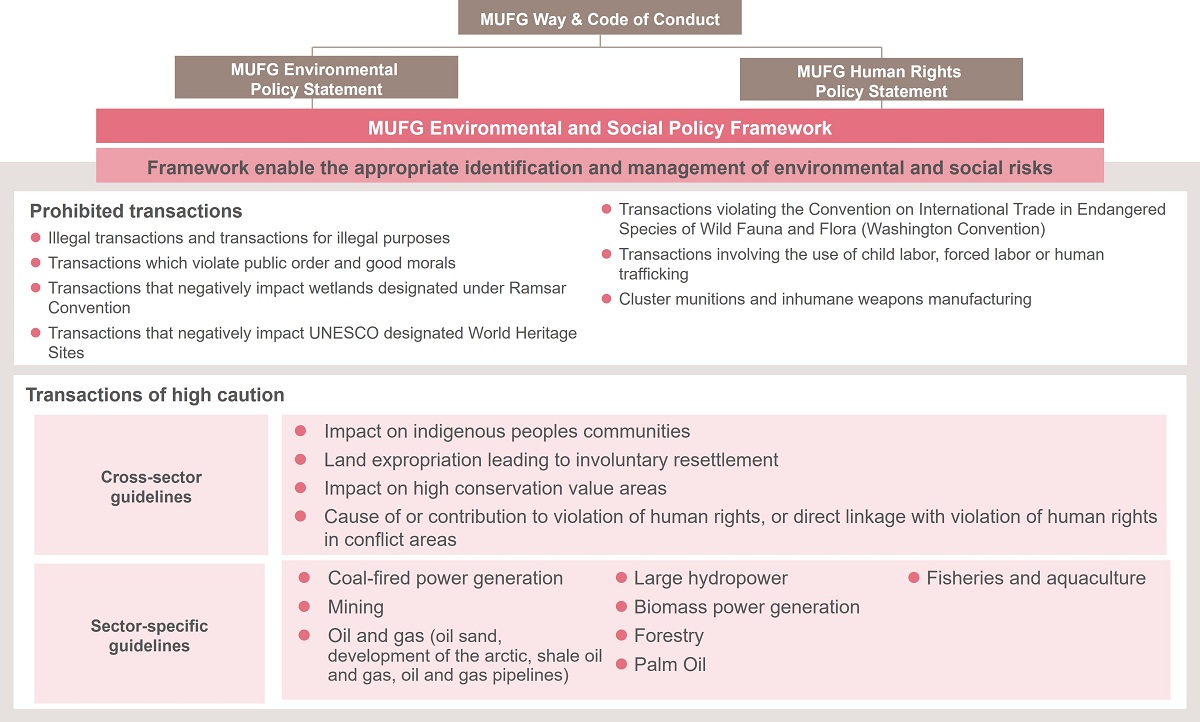
MUFG Environmental and Social Policy Framework
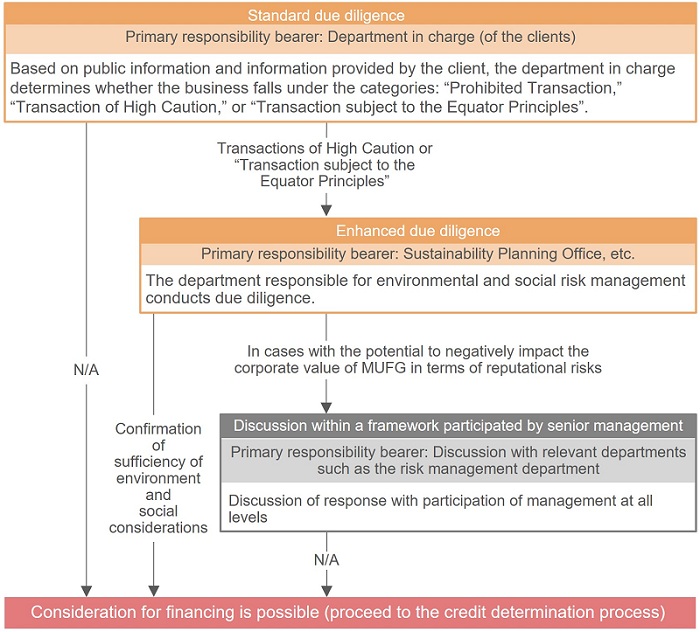
The Process of Identifying and Assessing the Environmental and Social Risks or Impacts of a Business to be Financed
Policies on the Sectors Related to the Environment, Including Climate Change
Response to Climate Change-Related Risks Based on the Equator Principles
The Equator Principles is an international framework developed to identify, assess, and manage the potential environmental and social risks and impacts of large-scale projects, including infrastructure and natural resource development. The Bank conducts environmental and social risk assessments based on the Principles prior to loan decisions.
Regarding climate change risks, in addition to examining technically and economically feasible options that contribute to reducing GHG emissions, the Bank evaluates the status of project developers' measures to identify and manage physical and transition risks in line with the TCFD recommendations.
Climate Change-Related Responses Required under the Equator Principles
| Applicable projects | Responses required under the Equator Principles |
|---|---|
Among the risk categories used in the Equator Principles, all Category A projects, and as appropriate, Category B(note) projects |
・Identification of physical risks and measures to manage those risks |
| Projects with GHG emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2), during its operational phase, of more than 100,000 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent per year | ・Alternatives Analysis ・Assessment of transition risks and countermeasures ・Annual public reporting of GHG emission levels |
- Category A refers to projects with potential significant adverse environmental and social risks and/or impacts that are diverse, irreversible, or unprecedented. Category B refers to projects with potential limited environmental and social risks and/or impacts that are few in number, generally site-specific, largely reversible, and readily addressed through mitigation measures.
Examples of Climate Change Risk Assessment
Physical risk (arterial road expansion project)
Physical risks identified in the assessment
・Increase in flooding and landslides associated with extreme rainfall causing damage to road facilities ・Increased frequency of bushfires (associated with increase in average temperatures) resulting in damage to motorway corridor and/or associated infrastructures |
Key actions taken by the project proponent
・Communication to contractors on increased likelihood of extreme rainfall and wind events occurring during construction; incorporation of extreme weather events in construction planning ・Adoption of a drainage design able to withstand projected extreme rainfall and flooding ・Augmented routine maintenance and inspections of structural components |
Transition risks (refinery expansion project)
Transition risks identified in the assessment
・New costs associated with GHG emissions e.g., introduction of carbon tax ・Increasing obligations against measuring and reporting GHG emissions ・Decline in demands for oil manufacturing services |
Key actions taken by the project proponent
・Evaluation of project economics with carbon tax (when introduced) ・Disclosure of climate-related risks and impacts on business and project’s initiatives to support low carbon transition ・Monitoring of global and emerging issues on the perceptions on oil and gas industry |

